Introduction
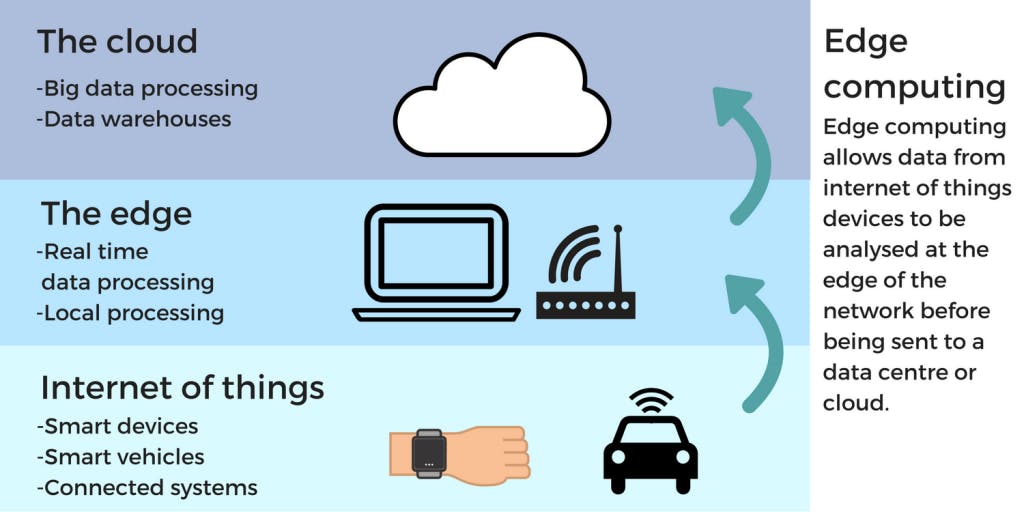
Edge Computing brings networked computing resources as near to the point of data creation as feasible. `Edge computing, as we'll see, is linked to the Internet of Things, mesh networks, and the use of tiny computer devices like shown below. So, let's take a closer look at computing at the network edge.
To comprehend edge computing, we must consider the emergence of the cloud. Hmmm...So do you know about Cloud Computing?
|

|
Brief introduction to Cloud Computing
a. What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing, which involves the supply of computer resources via the Internet, has become one of the most popular digital innovations in recent years.
- Cloud computing, which involves the supply of computer resources via the Internet, has become one of the most popular digital innovations in recent years.
- When you use a cloud computer, you may buy computing power, RAM, and storage on demand, as and when you need it. In this case, we don't want to own the IT infrastructure since it causes a slew of issues. It's adaptable, allowing us to select the appropriate amount and size of processing power and pay as we go based on how much we utilize the resources.
- It creates a scalable network of servers that can scale up and down as demand rises and falls.
b. Why Cloud Computing?
But Why!! Why do we need Cloud Computing
Practically if we look at it, When using standard server architecture, we must purchase resources as we scale up and down. It poses many issues since there may be a seasonal requirement, but you'll have to buy more servers and there will be enough server maintenance expenditures, such as server room rent, cooling charges, wiring fees, and employing personnel who can perform all of this. |


|
Cloud computing eliminates many of these drawbacks while also providing various additional benefits, like as
- It lowers capital costs and transforms them into operating expenses. So you don't have to buy a large server upfront; instead, you may pay as you utilize the resources, giving you much flexibility. As a consequence, the entire cost reduces.
- There's less guesswork since you can scale up or down your servers as needed, rather than guessing how many you'll need.
- There is no need to keep server rooms or provide physical space for these machines.
- In only a few minutes, you can be up and running with the cloud.
- Most clouds operate on a massive scale, allowing for economies of scale in pricing and maintenance.
c. Where does Edge Computing step in?
PCs and other end-user gear were the most common devices used to access cloud services in the early days.
However, gadgets that access cloud services are rapidly becoming the Internet of Things (IoT) appliances that transfer data for analysis online.
- The building of smart manufacturing and households is made effortless by integrating cameras and other detectors into the Internet. However, sending an increasing amount of data for remote, centralized processing gets difficult.
- Last but not least, sending video from web cameras to cloud-based vision recognition systems might cause network congestion and sluggish response times.
That is the reason why edge computing is becoming more popular.

So let's know more about Edge Computing 🤔
Introduction to Edge Computing
Edge Computing is a promising information technology (IT) architecture wherein client data gets processed nearest the source as feasible at the network's perimeter.
Modern businesses rely on data to provide significant business insight and real-time management over business operations and processes. Bulk data gets acquired routinely from sensors and IoT devices running in real-time from remote places and harsh working environments practically anywhere in the world, and today's most organizations are in an ocean of data.
🤩 Want to know more right! That is what the beauty of Edge Computing is!
 It's all about the location 🌍 when it comes to edge computing.
It's all about the location 🌍 when it comes to edge computing. Data is created at a client endpoint, including a user's computer, in traditional corporate computing. That data is sent through a wide area network (WAN), such as the internet, to the organizational LAN, where it is stored and processed by an enterprise. The work's results are subsequently sent back to the client's destination. It is still a tried-and-true client-server computing architecture.
However, the number of devices linked to the Internet and the bulk Data created. These are outpacing traditional data center infrastructures.
- Edge computing places memory and data centers where the data is. Requiring a small equipment rack to gather and analyze data locally across a distant LAN.
- In many situations, computer equipment is housed in shielded or hardened enclosures to protect it from temperature, humidity, and other external factors.
- Processing usually entails normalization and analyzation the data stream in search of business intelligence, with only the analysis' conclusions transmitted back to the primary data center.
Business intelligence may mean a lot of different things to different people. Retail establishments, for example, may integrate video monitoring of the showroom floor with actual sales data to identify the ideal product arrangement or consumer demand.
- Predictive analytics, for example, may be used to advise equipment maintenance and repair before real problems or breakdowns arise.
- Other instances are frequently associated with utilities.
- It includes water treatment or power production.
- It guarantees that equipment is in good working order and that output quality is maintained.
Why do we need to know about the Edge Computing
- Computing tasks necessitate appropriate designs, and architecture with one kind of computing activity may not be suitable for all sorts of computing tasks.
- Edge computing has developed as a feasible and essential architecture for distributed computing, allowing computation and storage resources to be deployed closer to the data source, preferably in the physical location.
- In general, distributed computing models aren't new, and the notions of remote offices, branch offices, data center colocation, and cloud computing are well-established.
Decentralization, on the other hand, can be difficult. It necessitates a high degree of management, and surveillance. It disregards when drifting away from a typical centralized computer approach.

Limitations of Edge and Fog Computing
Take, for example, the emergence of self-driving automobiles. Intelligent traffic control signals will be required. Automobiles and traffic control systems will have to produce, analyze, and share data in real-time. When you increase this requirement by many autonomous cars, you can see the scale of the possible issues. It needs a network that is both quick and responsive.
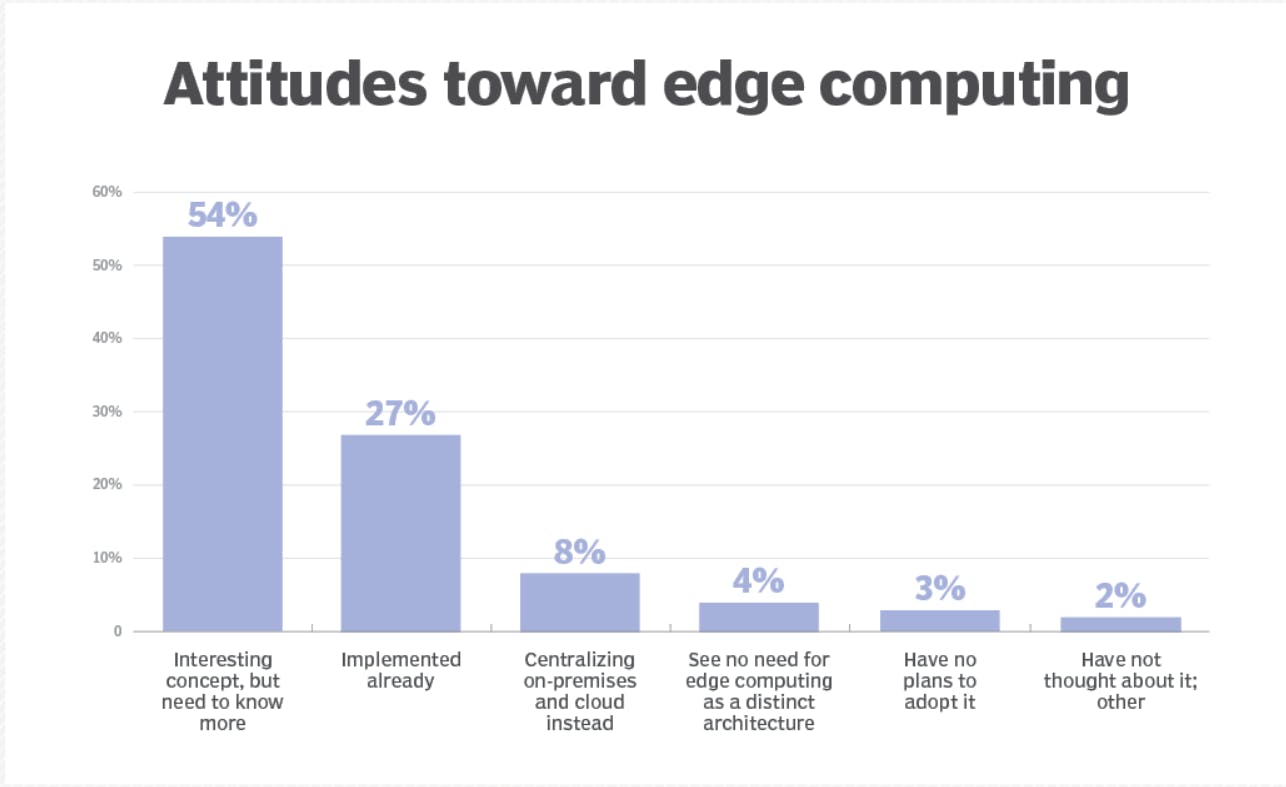
Four major network limits are addressed by edge and fog computing: 1. Bandwidth 2. Latency 3. Congestion 4. Dependability.
- Edge computing operates several devices across a much smaller and more efficient LAN where abundant bandwidth is used entirely by local data-generating devices, effectively eliminating delay and congestion.
- Local storage captures and secures raw data, while local servers may execute critical edge analytics — or at the very least pre-process and minimize data — in real-time to make choices before transferring findings, or merely relevant data, to the cloud or central data center.
Edge Computing: Use cases and Examples in the Real World

1. Manufacturing - Edge computing was used by an industrial company to monitor manufacturing, allowing real-time analytics and machine learning to be performed at the edge to identify production mistakes and enhance product quality. The deployment of environmental sensors throughout the production plant is aided by edge computing. It provided information into how each product component is built and kept, and how long the components are in stock.
2. Farming - Consider a company that produces vegetables without sunshine, soil, or pesticides inside. Grow times are reduced by more than 60% with this method. The company can measure water usage, nutritional density, and predict the best harvesting time by using sensors. Data is gathered and evaluated to determine the impacts of environmental conditions, optimize agricultural growing algorithms, and guarantee that crops are harvested in optimal condition.
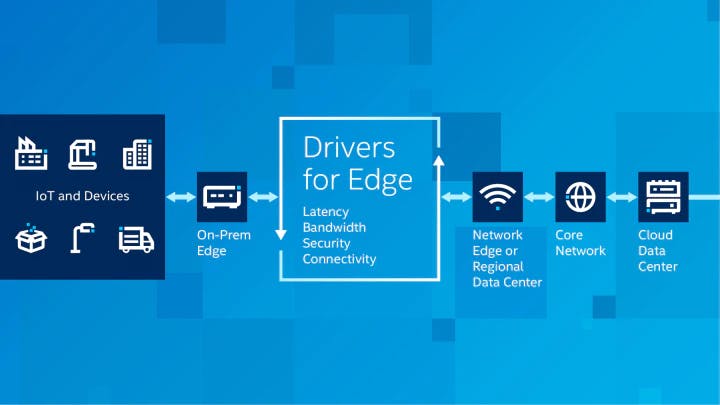
3. Optimization of the network - By evaluating network performance for users throughout the internet and using analytics to discover the most reliable, low-latency network channel for each user's data, edge computing can enhance network performance. In effect, edge computing is used to "steer" traffic around the network to get the best possible performance for time-sensitive traffic.
4. Workplace security is important - Edge computing can combine and analyze data from on-site cameras, employee safety devices, and a variety of other sensors to help businesses monitor workplace conditions or ensure that employees follow established safety protocols, particularly in remote or potentially dangerous environments like construction sites or oil rigs.
5. Healthcare - The amount of patient data acquired via devices, sensors, and other medical equipment has increased tremendously in the healthcare business. This massive data volume necessitates the use of edge computing to access the data, disregard "normal" data, and detect issue data. These physicians may intervene in real-time to assist patients to prevent health crises.
6. Transportation - Autonomous vehicles use and create anywhere from 5 to 20 TB of data each day, collecting data on their position, speed, vehicle condition, road conditions, traffic conditions, and other vehicles. And when the vehicle is in motion, the data must be pooled and processed in real-time. It necessitates a substantial amount of onboard processing since each autonomous vehicle acts as an "edge."
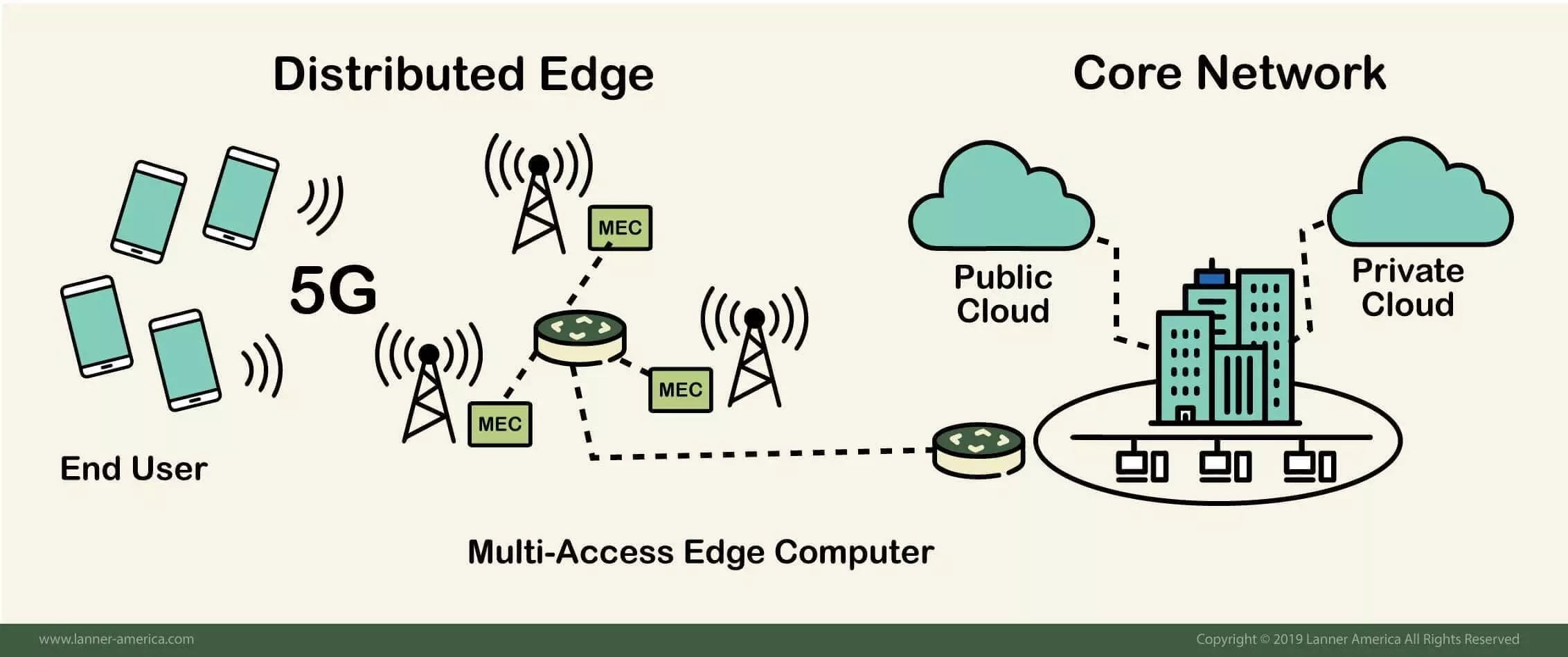
Edge Computing: Possibilities in IoT, 5G

|
|
Edge availability is perhaps the most notable development, with edge services predicted to be available worldwide by 2028.
Whereas today's edge computing is frequently situation-specific, the technology is predicted to become more pervasive and change the way people use the internet, bringing with it more abstraction and possible use cases.
The growth of computing, storage, and network appliance devices developed expressly for edge computing demonstrates this. At the edge, more multivendor alliances will improve product interoperability and flexibility. Cooperation between AWS and Verizon, for example, is bringing improved connections to the edge.
- In the coming years, wireless communication technologies like 5G and Wi-Fi 6 will have an impact on edge deployments and usage, facilitating virtualization and mechanization capabilities that have yet to be researched, such as better vehicle individuality and workflow relocations to the edge, while attempting to make wireless devices more flexible and cost-effective.
- With the development of IoT and the resulting avalanche of data that such devices generate, edge computing has gained traction. However, because IoT technologies are still in their infancy, the evolution of IoT devices will influence edge computing's future development. The creation of mini modular data centers is one example of such future options.
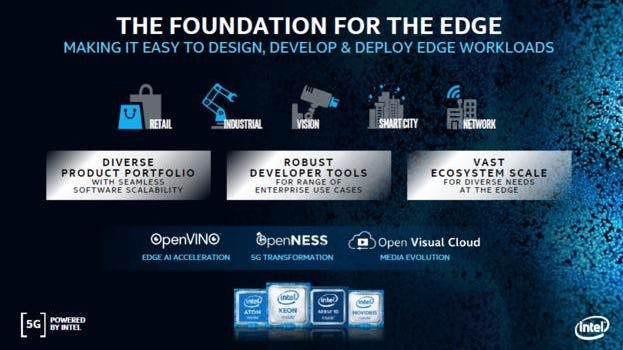
How is Intel paving its way in Edge Computing
The development of distributed edge solutions is one of the most difficult tasks. Intel's focus on open platforms and assistance for containerized and cloud-native development helps streamline workflows and expedite deployment.
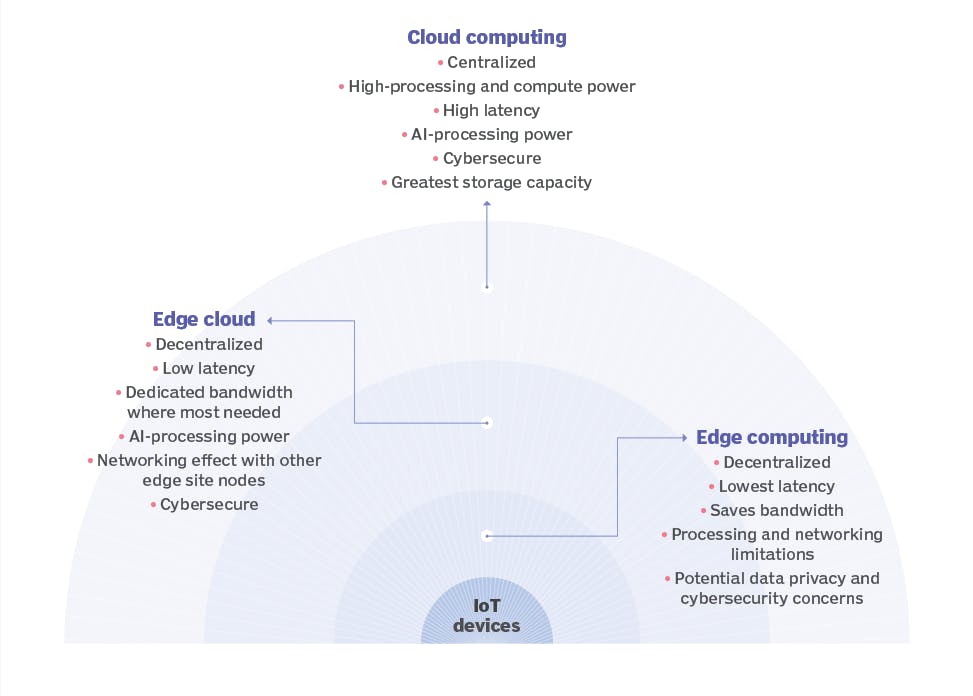
Edge Cloud - Cloud computing has radically changed the way organizations of all kinds operate. For specific types of workloads, such as latency-sensitive apps, organizations are now supplementing cloud computing with edge computing. Edge cloud computing brings the cloud's ease to edge networks. Micro-data centers host edge clouds, which store, analyze, and process data quicker than a link to a data center allows.
Intel's Edge Ready Hardware - Intel proudly delivers the most diversified edge-ready computing, networking, memory, and storage solutions in the world, from smart cameras to base stations to hyper-converged "data centers in a box." For instance, IoT and Embedded Processors, Intel® FPGAs, Intel® Xeon® Processors, Intel® Movidius™ VPUs, etc.
Intel Edge Software Hub - The Intel Edge Software Hub is a one-stop-shop for IoT development tools and resources. It provides tools and software packages that may be quickly deployed to scale to large-scale IoT systems. These resources have also been thoroughly pretested and prevalidated to assure quality and dependability, while also serving as a strong complement to Intel's large hardware range in an integrated IoT ecosystem.
Intel's Edge Computing Certification - Hands-on experience with edge AI tools and platforms, such as the Intel® Distribution of OpenVINOTM toolkit and Intel® DevCloud, is part of the certification course. Use cases that use computer vision and deep learning inference to detect safety gear, avoid retail losses, identify manufacturing faults, and handle other real-world challenges. Develop your edge AI solution portfolio, based on libraries and APIs for TensorFlow, PyTorch, Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX*), and other open models, and operating on Intel® DevCloud hardware clusters of your choosing.
Phew.. that was a lot.

Thank you for reading my attempt at explaining how you could get started with Edge Computing. Please feel free to comment your views on the same, do you feel Edge Computing has such a potential for upcoming future technologies?
Also, feel free to give this a thumbs up, and share it with your known ones so that more and more people get to know about Edge Computing! 🤗
Hariket Sukesh Kumar Sheth, Intel Student Ambassador Team (VIT Chennai)

